
Smart Contract Benefits & Risks Simplified for Success
Smart Contract Benefits & Risks Simplified for Success. Explore types, uses, risks, tax, and how to qualify and maximize their impact across industries.
What is a Smart Contract?
A Smart Contract is a self-executing digital agreement that operates on Blockchain technology. It runs automatically when specific conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries such as lawyers or brokers. These contracts are written in code and stored on a decentralized blockchain, making them immutable and tamper-proof.
Smart contracts are trusted for their ability to execute predefined actions securely and efficiently, providing assurance that all parties involved will uphold the terms without requiring manual enforcement.
Read All About In Details: Smart Contracts Explained
Types of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts come in different forms, depending on their design and purpose:
- Public
Accessible to anyone on public blockchains like Ethereum. Used in decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi, and NFTs. - Private
Run on permissioned blockchains where only selected users can interact. Common in corporate environments. - Hybrid
Combine on-chain code with off-chain data and services, allowing greater flexibility and application in real-world scenarios. - Oracle-Based
Use external data feeds (oracles) to trigger execution. Ideal for contracts relying on real-world information like weather or market prices.
Common Use Cases in Different Industries
Smart digital agreements are transforming industries by enabling trustless automation and efficiency. In finance, they handle lending, trading, and payments with zero manual intervention. Healthcare uses them for secure patient data access and insurance claims processing. In real estate, they simplify property transfers and escrow handling. Supply chain companies deploy them to track goods, authenticate products, and trigger payments. Even in entertainment, musicians and creators receive automatic royalty payments. These diverse use cases show how programmable agreements reduce overhead, build transparency, and eliminate the need for centralized control—making them essential in the evolving digital economy.
Why Do Companies Offer Smart Contracts?
Companies adopt smart contracts to reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, and build trustless systems that don’t rely on third-party enforcement. Here’s why they are widely implemented:
- Automation: Enables seamless execution of tasks like payments, asset transfers, and recordkeeping.
- Security: Reduces fraud through blockchain’s immutable nature.
- Transparency: All participants have real-time access to contract terms and outcomes.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates middlemen such as brokers or legal agents.
- Reliability: The deterministic logic ensures contracts execute exactly as written.
From fintech to real estate and supply chains to insurance, businesses use smart contracts to streamline processes and enhance productivity.
Read All About what IBM says on: What are smart contracts on blockchain?
How to Qualify for Smart Contract Use
To use or deploy a smart contract, the following is generally required:
- Blockchain Access: You need to work within a blockchain ecosystem such as Ethereum, Solana, or Polygon.
- Crypto Wallet: Tools like MetaMask are necessary to interact with and authorize smart contract transactions.
- Basic Technical Understanding: While end-users don’t need to code, businesses deploying contracts need developers proficient in Solidity, Rust, or similar languages.
- Regulatory Awareness: Understand the legal framework surrounding digital contracts in your jurisdiction.
- Auditing Tools: Always audit custom contracts using third-party tools or services to ensure code security and efficiency.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer many distinct advantages:
- Efficiency: Tasks are completed in seconds without human involvement.
- Trustless Transactions: No need to rely on third-party validation—just the contract code.
- Accuracy: Eliminates errors from manual processing.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces legal and administrative expenses.
- Scalable: Suitable for high-frequency, high-volume transactions.
- Immutable & Secure: Once deployed, the contract cannot be changed, offering confidence and transparency.
These features make smart contracts a robust solution for businesses looking to modernize operations and boost customer trust.
Real-World Adoption Example
Many global companies are now implementing blockchain-based digital agreements to streamline operations. For instance, logistics firms use them to automate supply chain updates, ensuring real-time tracking and transparent delivery records. Insurance providers leverage them for instant claim approvals, reducing paperwork and processing delays. Even in real estate, digital contracts are used to simplify property transactions and eliminate third-party fees. This real-world adoption highlights the growing trust in decentralized automation and sets the stage for widespread usage across sectors looking to improve security, cut costs, and eliminate manual bottlenecks.
Risks and Precautions
Despite their benefits, smart contracts are not risk-free:
- Code Errors: Bugs in contract logic can lead to financial losses or manipulation.
- Immutability: Once deployed, flawed contracts cannot be altered.
- Oracle Manipulation: If external data sources are compromised, contract behavior may be affected.
- Legal Ambiguity: Not all jurisdictions recognize or regulate contracts effectively.
Precautionary Tips:
- Use audited templates and frameworks.
- Test contracts on testnets before live deployment.
- Choose decentralized, verified oracle providers.
- Keep a complete record of interactions and wallet transactions.
Where to Find Legit Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are hosted on several reputable blockchain platforms:
- Ethereum: Most widely used for DeFi and NFT projects.
- Polygon: A layer-2 Ethereum solution offering faster, cheaper transactions.
- Binance Smart Chain: Known for its low transaction fees and fast processing.
- Solana: Popular for its speed and scalability in complex applications.
Legit smart contracts often come with public code repositories and community or third-party audits. Open-source libraries like OpenZeppelin also provide secure, reusable contract templates.
Best Strategies to Maximize Smart Contract Use
- Start with Pre-Built Contracts: Use secure, proven templates to avoid vulnerabilities.
- Modular Design: Write flexible code for easy upgrades.
- Use Multi-Sig Wallets: Add extra layers of authorization for contract execution.
- Optimize Gas Usage: Keep your code lightweight to reduce transaction costs.
- Integrate Secure Oracles: Use services like Chainlink for trusted external data feeds.
- Conduct Periodic Audits: Regular reviews help catch security flaws early.
Implementing these strategies helps businesses gain the most from smart contract deployment while minimizing exposure to risk.
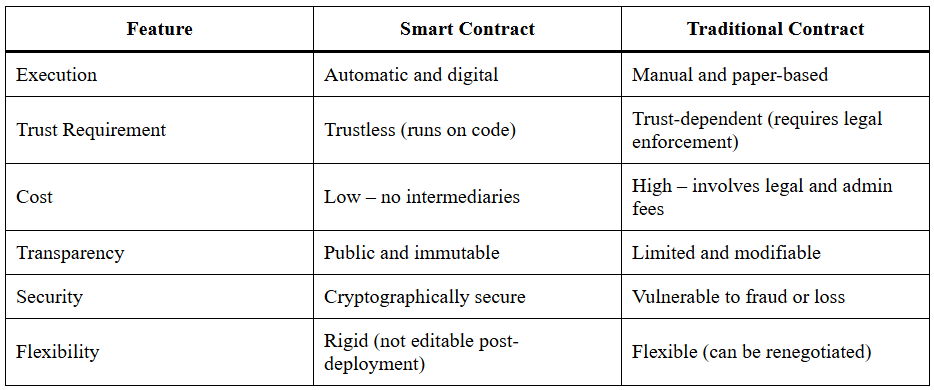
Smart Contract vs Traditional Contract
Tax Implications
Smart contracts themselves aren’t taxed, but the financial activities they perform often are:
- Crypto Swaps: Subject to capital gains tax.
- Yield Farming/Staking: Considered income in many jurisdictions.
- NFT Transactions: May be taxed based on gains or royalties.
- Airdrops & Token Rewards: Often classified as income.
Maintain accurate records of all smart contract interactions. Consult a tax advisor familiar with blockchain to ensure full compliance.
Future Outlook
Smart contracts are expected to power the next wave of digital transformation. Innovations on the horizon include:
- AI-Powered Contracts: Adaptive contracts using real-time data and decision models.
- Cross-Chain Contracts: Interoperable contracts that work across multiple blockchains.
- Legal Integration: More countries are moving toward legal recognition of contracts.
- Enterprise Adoption: Corporates are integrating blockchain solutions into legacy systems using smart contracts.
As technology evolves, smart contracts will drive automation, accountability, and transparency across every sect, from banking to public governance.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are revolutionizing how digital agreements are created and enforced. Their ability to execute automatically, securely, and transparently makes them a game-changer for modern businesses. While challenges like bugs, security risks, and legal issues remain, their benefits outweigh the risks when used correctly. By understanding how to use, qualify for, and optimize smart contracts, individuals and companies can position themselves for long-term success in the blockchain era.
I work as a content writer in the blockchain and cryptocurrency domain. I have a keen interest in exploring the world of digital assets, Web3, and emerging crypto technologies. My goal is to provide readers with easy-to-understand, engaging, and trustworthy insights, helping them stay informed and confident in the rapidly evolving world of crypto and blockchain.





