The concept of Proof Of Work In Blockchain has become a cornerstone of cryptocurrency infrastructure, especially in networks like Bitcoin. Proof of Work (PoW) is a foundational mechanism that enables secure, trustless transactions across decentralized networks, eliminating the need for any central governing body. Known for its robust security and transparent operation, PoW also raises critical questions about energy efficiency and scalability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down how PoW functions, trace its origins, examine its advantages and limitations, and explore its relevance in the ever-evolving blockchain ecosystem.
What Is Proof Of Work In Blockchain?
Proof of Work (PoW) is a blockchain consensus protocol designed to maintain the security and accuracy of transactions while enabling the creation of new blocks within the distributed ledger. In this system, participants called Miners compete to solve intricate mathematical puzzles. The miner who successfully solves the problem first shares the solution with the network. After verification by other nodes, the new block is officially added to the blockchain.
This mechanism allows all nodes in a decentralized network to reach consensus on a unified version of the blockchain, eliminating the need for any central authority. It plays a crucial role in preventing fraudulent activity and maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the distributed ledger.
How Does Proof Of Work In Blockchain Function?
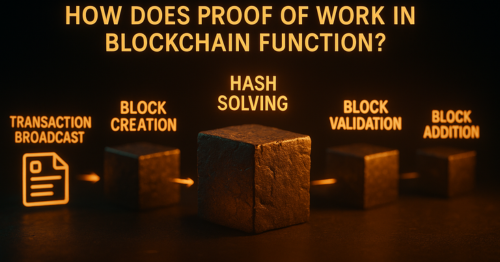
- Transaction Broadcast: All pending transactions are broadcast to the network.
- Block Creation: Miners collect transactions and try to create a new block by solving a cryptographic puzzle (hashing).
- Hash Solving: The goal is to find a hash below a certain difficulty target. This process is resource-intensive and requires trial and error.
- Block Validation: Once a valid hash is found, it is verified by other miners.
- Block Addition: The verified block is added to the blockchain, and the successful miner earns a reward.
This process makes tampering with past transactions extremely difficult since changing one block would require re-mining all subsequent blocks, which is practically impossible without massive computing power.
Who Created Proof Of Work In Blockchain?
The concept of Proof Of Work In Blockchain was popularized by Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, in the Bitcoin whitepaper released in 2008. While the concept of PoW predates Bitcoin and was initially used to combat email spam and denial-of-service attacks, Nakamoto applied it ingeniously in the blockchain context to enable decentralized consensus.
- Founder: Satoshi Nakamoto (pseudonym)
- Establishment Year: 2008 (Bitcoin Whitepaper Release)
This model was first implemented in Bitcoin, which officially launched in January 2009 and has since become the gold standard for decentralized cryptocurrencies.
Benefits of Proof Of Work In Blockchain
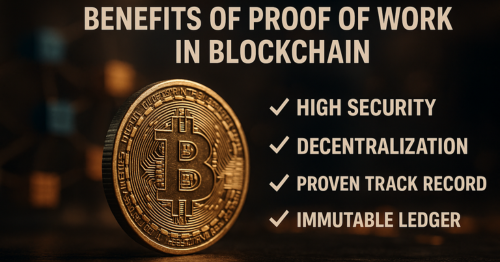
High Security
Due to its computational difficulty, PoW offers strong protection against tampering and double-spending. It has stood the test of time against multiple attack attempts.
Decentralization
Anyone with enough computing power can join the network, reinforcing Decentralization and resisting censorship or centralized control.
Proven Track Record
Bitcoin, Ethereum (before its switch to PoS), and many other networks have successfully used PoW for over a decade.
Immutable Ledger
Changes to past transactions require enormous computational resources, making it virtually impossible to alter the blockchain.
Drawbacks of Proof Of Work In Blockchain
High Energy Consumption
Mining consumes a vast amount of electricity. According to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Bitcoin’s annual energy usage rivals that of some entire nations.
Expensive Equipment
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) and high-end GPUs are costly, creating high entry barriers for new participants.
Centralization Risks
Large mining pools control a significant share of mining power, raising concerns about centralization and potential manipulation.
Limited Scalability
Due to slow block creation and high energy requirements, PoW is less scalable compared to newer consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake.
Proof Of Work vs. Proof Of Stake
While Proof Of Work In Blockchain remains secure and time-tested, the ecosystem is gradually shifting toward Proof of Stake (PoS) due to environmental concerns and scalability. Ethereum’s shift from PoW to PoS with its Merge in 2022 reflects this broader trend in the crypto world.
Real-World Application of Proof Of Work In Blockchain
- Bitcoin (BTC): The most prominent example of PoW, securing billions of dollars in value and facilitating millions of transactions worldwide.
- Litecoin (LTC): A faster, more lightweight version of Bitcoin, also using PoW for security and consensus.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH): A Bitcoin fork that retains PoW but with larger block sizes for faster transaction throughput.
Why Proof Of Work Still Matters
Despite growing criticism, Proof Of Work In Blockchain remains one of the most trusted and time-tested methods for achieving distributed consensus in public blockchains. For high-value assets like Bitcoin, where trust, security, and immutability are critical, PoW offers unmatched reliability.
Moreover, for individuals entering the blockchain space, whether as traders, developers, or institutional investors, understanding the core mechanics of PoW is essential. It lays the foundation for all modern blockchain applications.
The Future of Proof Of Work In Blockchain
The growing demand for sustainable solutions has prompted many networks to explore alternatives to PoW. However, it is unlikely that PoW will disappear completely. Innovations such as renewable-powered mining farms, merged mining, and second-layer scaling solutions are helping make PoW more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Bitcoin, the flagship cryptocurrency, is expected to remain on PoW for the foreseeable future. It is designed around this model, and the community values its robustness and resistance to change. However, we may see new hybrid models in the future that combine the benefits of PoW and PoS.
Related Reading
Check out our detailed article on How Blockchain Technology Works to understand the fundamentals behind decentralized systems.
Authority Resource
To explore more about PoW’s energy consumption data, refer to the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance.
Conclusion
Proof Of Work In Blockchain has shaped the foundation of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. From powering Bitcoin to inspiring newer consensus mechanisms, it stands as a pioneering solution to the problem of digital trust. Despite its high energy costs and scalability concerns, PoW remains the most secure and proven system for decentralization.
Understanding Proof Of Work In Blockchain is essential for anyone serious about crypto—whether you are trading, building, or simply exploring the space. As the blockchain landscape evolves, PoW’s role may shift, but its legacy will continue to influence the design and operation of decentralized networks worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Proof Of Work in blockchain and how does it work?
Proof Of Work in blockchain is a consensus mechanism where miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. This process ensures network security and decentralization by requiring computational effort before a block can be confirmed.
Why is Proof Of Work important in blockchain technology?
Proof Of Work is important because it prevents double-spending, secures the blockchain from malicious attacks, and eliminates the need for centralized authorities. It provides a trustless environment where participants can agree on the state of the ledger without intermediaries.
Which cryptocurrencies use Proof Of Work?
Popular cryptocurrencies that use Proof Of Work include Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and Bitcoin Cash (BCH). Ethereum used PoW until 2022 before transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS).
What are the disadvantages of Proof Of Work in blockchain?
The main disadvantages of Proof Of Work include high energy consumption, expensive mining hardware requirements, centralization risks from mining pools, and limited scalability due to slower transaction speeds compared to newer consensus models.

I work as a content writer in the blockchain and cryptocurrency domain. I have a keen interest in exploring the world of digital assets, Web3, and emerging crypto technologies. My goal is to provide readers with easy-to-understand, engaging, and trustworthy insights, helping them stay informed and confident in the rapidly evolving world of crypto and blockchain.










