Liquid Staking Vs. Traditional Staking: Earn Smarter with Crypto. Crypto staking is an emerging concept in India that has simplified passive income strategies without requiring high capital investments or active trading. With the increased adoption of crypto assets, another staking approach that has gained prominence in recent years is liquid staking.
Both staking models allow you to grow your crypto holdings, but are they the same? No, there are some clear differences. Each of them has specific characteristics and considerations catering to the unique needs of different users.
This blog elaborates on traditional and liquid staking, their key differences, benefits, and limitations, and how each strategy can align with your crypto earning plans. Let’s begin.
Navigating Traditional Staking
Traditional staking involves committing or locking your crypto holdings (stake) in a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain network to support its operations, validate transactions, and enhance network efficiency.
The staked assets act as collateral where the crypto validators pledge their holdings to the network. This enhances their reliability and ensures they work responsibly and perform their staking operations correctly.
If a validator violates the trust, goes offline frequently, or fails to perform the staking process correctly, the PoS network may “slash” or take away a portion or the entire staked holdings. In this context, a risk of loss guarantees that the validators work honestly and do not compromise network security and efficiency.
The Traditional Staking Lifecycle:
How to stake and earn through traditional staking:
- Buy token: The first step is to buy the native token of the PoS network from a valid crypto exchange. Not all crypto assets support staking. Choose a crypto like ETH (Ethereum) or DOT (Polkadot) that supports PoS or a related consensus mechanism.
- Staking platform: Depending on the type of staking, like custodial or non-custodial, you must select an appropriate staking platform. Consider the platform fees, lock-up period, reputation, and other details.
- Select wallet: Connect to a designated crypto wallet that supports the staking platform to receive staking rewards. Example – MetaMask, Tezos, Ledger, etc.
- Stake tokens: Lock up crypto holdings for staking. Certain prerequisites are required to run a validator node or qualify as a network validator. Blockchain networks like Ethereum need 32 ETH minimum holdings to qualify. Furthermore, if you participate in active staking like solo-staking, you must meet certain technical and operational criteria for approval.
- Validation process: Validators are chosen randomly from a queue. However, it also depends on the staked amount. Validators with substantial or high crypto holdings have greater chances of being selected. As a validator, you must perform certain tasks to earn rewards.
- Staking rewards: The network incentivizes you with staking rewards for adding a block and validating transactions. This reward is proportional to the staked amount and the lock-up period and is transferred to the supported wallet.
- Unstaking and withdrawal: Once you initiate the unstaking process, you will be put in the withdrawal queue. After the waiting period or “unbonding period,” you can withdraw the funds.
Key Points:
- The crypto holdings staked are locked up during the staking period.
- Staking requires a minimum amount to qualify.
- Staked crypto holdings are illiquid and cannot be used for trade or other DeFi operations.
- Certain types of crypto staking, like solo-staking, require technical expertise.
- Validators may face “slashing” and pay penalties for misbehaving, breaking network rules, fraud, or poor performance.
Benefits and Risks of Traditional Staking for Crypto Investors
Benefits
- Stable and long-term yields: Staking offers high returns of around 4-10%, greater than banking interest in India, depending on how the validators perform. You can also re-stake and earn compounding rewards, generating steady long-term returns.
- Earn passively with idle crypto: Staking generates an alternative source of income simply by locking crypto holdings without actively participating in direct trading.
Risks
- Illiquidity: Traditional staking locks the funds for a specific period. During this time, the staked assets cannot be accessed, transferred, traded, or used in other DeFi (decentralized finance) operations.
- Slashing: PoS networks like Ethereum impose penalties called slashing for inactivity, misbehaviour, malicious activities, or if validators are offline. This penalty is deducted from the staking rewards. This impacts both the validator and the delegator.
- Withdrawal queue: The unstaking process is lengthy. Validators in the Ethereum network have to wait for their turns in the withdrawal queue before they can finally withdraw their staking rewards, which can be time-consuming.
- Technical expertise: Solo-staking requires high technical expertise, hardware requirements, uninterrupted internet connectivity, and market knowledge. This may be challenging for novice investors, especially in countries like India, where staking is still an unfamiliar territory compared to traditional financial investments.
- Investment threshold: Certain blockchain networks, like Ethereum, have an entry barrier to qualify as a validator. For example, the minimum crypto holdings or investments in Ethereum is 32 ETH. Direct or active staking involves hardware setup, electricity consumption, and internet connectivity, which can be expensive for small-time investors.
Understanding Liquid Staking
Liquid staking has gained popularity as a more flexible alternative to traditional staking. Here, you do not completely lock the funds, maintaining the liquidity of the staked assets.
How does it work?
Rather than directly staking in the PoS network, you stake through a liquid staking protocol like Rocket Pool or Lido, or a liquid staking platform like Stader Labs that supports multiple blockchains and allows users to access the protocols.
These protocols or platforms issue a tokenized version of the staked assets called LSTs (liquid staking tokens). For example, stETH (staked Ether issued by Lido Finance) or cbETH (issued by Coinbase). These LSTs represent derivative tokens that are free and illiquid and can be used for transfer, trading, buy, or sell, and other DeFi operations without affecting the underlying staked amount.
In this way, liquid staking bypasses the major inconvenience or limitation of traditional staking, the “lock-up” period or “illiquidity” by making staked assets accessible.
Liquidity Staking Lifecycle:
- Deposit tokens: Acquire the PoS tokens you want to stake, like ETH (Ethereum) or SOL (Solana), and deposit them into the liquid staking protocol. The protocol selects validators who stake the tokens.
- Receive LSTs: The protocol issues LSTs that represent the staked assets. These tokens can be traded, transferred, or used in DeFi applications.
- Earn rewards: The Value of LSTs automatically accrues over time and is reflected in your wallet. For example, 100 LSTs may grow to 110 LSTs after a year. Here, the difference of 10 LSTs is the staking reward.
- Optimize earnings: Multiply earnings through trading, lending, or yield farming LSTs in decentralized (DEX) or centralized (CEX) platforms.
- Exit plan: You can unstake or redeem the LSTs and staking rewards at any time. Every protocol has an unbonding or waiting period. After the waiting period, users get the accumulated rewards plus the underlying staked amount (original holdings).

Benefits and Risks of Liquid Staking for Crypto Investors
Benefits
- Unlocks liquidity: One of the greatest benefits of liquid staking is that it retains the liquidity of the staked crypto assets. It generates LSTs representing the underlying staked amount that can be accessed, traded, or used in liquidity pools or yield farming. You can restake the rewards and enhance your overall crypto earnings.
- Enhances accessibility: While your crypto holdings are being staked, liquid staking issues derivative tokens or LSTs simultaneously that can be accessed at any time and used in other DeFi operations.
- Low entry barrier: There is no fixed minimum investment in liquid staking or to qualify as a validator. You can start staking with small amounts. It is ideal for Indian investors with limited capital who want to participate in staking.
- Reduces opportunity cost: The tokenized staked assets or LSTs can be used or traded elsewhere. This improves potential gains without sacrificing staking rewards.
- Multiple earning streams: Crypto stakers benefit by using LSTs in liquidity pools, trading, or yield farming, generating multiple passive income streams.
- Ideal for beginners: Liquid staking is done through a liquid staking protocol or platform. Simply deposit the funds and start earning. It does not require technical expertise or hardware setup.
Risks
- Counterparty risks: Since liquid staking is done through a third-party service provider involving external validators, you must consider counterparty risks or security issues. Verify and check the platform’s reputation before staking.
- Validator performance: Validators’ performance can impact staking rewards. If validators perform poorly or indulge in fraudulent activities, the network may slash or penalize them, resulting in loss of funds.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities: Liquid staking platforms operate through smart contracts, which may be susceptible to security issues, bugs, or poor audits.
- Price de-pegging: LSTs are subject to price de-pegging and market fluctuations, which may reduce the price of the staked assets below the pegged value and the fair market value.
Liquid Staking Vs. Traditional Staking: Earn Smarter with Crypto
There is no doubt that liquid staking offers flexibility and capital efficiency compared to traditional staking. The returns are not limited to staking rewards. Investors can multiply passive income earnings with LSTs. However, choosing the right type of staking also depends on the investor’s unique needs and choices.
A tech-savvy crypto enthusiast familiar with the staking process may want to control asset ownership and prefer traditional staking. On the other hand, liquid staking offers higher rewards and is suitable for novice traders or investors who do not want to get involved in the direct staking process.
Let’s break down the key differences:
Liquid Staking Vs. Traditional Staking
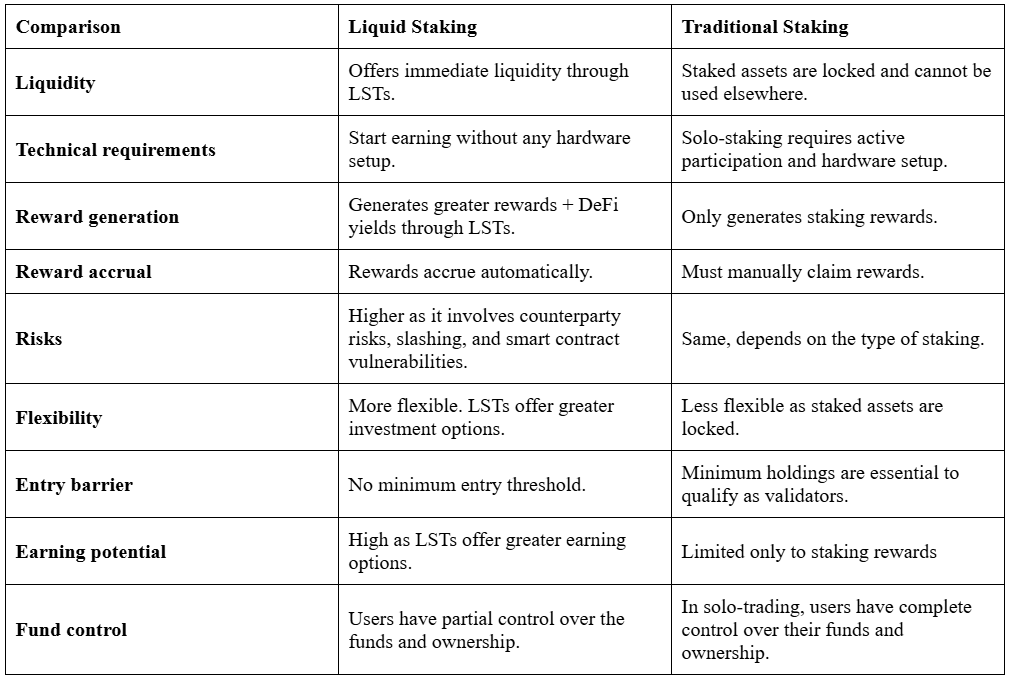
When should you choose traditional staking?
- You prefer conventional staking methods.
- Comfortable with locking funds for a long duration.
- Have substantial holdings for staking.
- Only want to stake. Not interested in LSTs or other DeFi operations.
When should you choose liquid staking?
- You want to start small with limited funds.
- Explore flexible and innovative strategies to boost crypto earnings through LSTs and DeFi applications.
- Do not want to lock your funds for a long time.
- Comfortable in taking risks and earning extra rewards.
Final Thoughts
Both liquid staking and traditional staking offer valuable sources of passive income with crypto. The right strategy depends on your investment goals, resources, technical acumen, and risk tolerance. Someone aiming for steady long-term returns, traditional staking is a good fit. On the other hand, liquid staking presents flexibility, capital efficiency, and greater returns. It is more inclusive, does not require high capital investments, and offers multiple earning streams.
Both staking models have their merits and limitations. If you are new to crypto staking, research and consider the risk factors and financial objectives, and ensure they align with your broader investment strategies and goals.

Taniya is a Content Writer with over 6 years of experience in the industry, specializing in Web3, crypto, Blockchain, Tokenization, and Decentralized Finance. She is passionate about creating compelling and well-researched narratives, navigating readers through the emerging trends and dynamic world of Web3 and Decentralized Finance.










