Tax On Crypto In India: The Harsh Truth Uncovered. Understanding how digital assets are taxed is crucial for every trader and investor navigating the Indian crypto landscape. The Indian government has laid out a clear but strict taxation structure for cryptocurrencies, impacting how profits are reported and taxed. Whether you’re a casual investor or a full-time crypto trader, grasping the nuances of Tax On Crypto In India can save you from future penalties and compliance issues.
What Is Tax On Crypto In India?
India officially recognized cryptocurrencies as Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) in 2022 through the Union Budget. This came with a dedicated taxation framework targeting crypto earnings. Unlike traditional assets, crypto profits are treated differently and often more harshly under Indian tax laws.
The Tax On Crypto In India is built around two key pillars:

- 30% Flat Tax on Gains
The Tax On Crypto In India enforces a 30% flat tax, along with applicable surcharge and cess, on income earned through the transfer of crypto assets. Only the cost of acquisition can be deducted. - 1% TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
Under the Tax On Crypto In India, starting July 1, 2022, a 1% TDS is deducted on every crypto transaction above ₹10,000 within a financial year. This is deducted at the source (e.g., exchange platforms) and applies whether you make a profit or not.
Additionally, it’s important to note that even airdrops, staking rewards, and crypto gifts may fall under the Tax On Crypto In India, depending on how the income is received.
Read All About: Crypto Tax In India
Who Needs to Pay Tax On Crypto In India?
Anyone who engages with crypto in any capacity may be liable to pay Tax On Crypto In India, including:
- Individual investors and traders
- Businesses accepting crypto as payment
- NFT artists and developers
- Freelancers earning in crypto
- Crypto miners selling mined coins
Even if your crypto-related income is irregular or small, it must be reported. The Indian government monitors exchanges, PAN-Aadhaar links, and wallet activity for tax compliance. Non-reporting could result in penalties or audits.
How Is Crypto Income Categorized in India?
The Income Tax Department does not treat crypto as capital gains. Instead, income from crypto is classified under a special category of virtual digital assets. Below is a breakdown of how activities are taxed under Tax On Crypto In India:
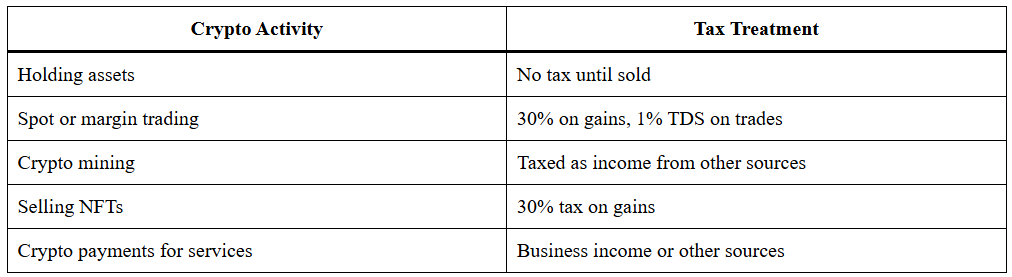
This approach makes crypto more heavily taxed compared to traditional assets like stocks or gold, where loss set-offs and deductions are allowed.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Misunderstanding or misapplying the Tax On Crypto In India can lead to serious trouble. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
- Failing to report peer-to-peer transactions
- Declaring gains under the wrong income head
- Ignoring the 1% TDS requirement
- Not maintaining cost acquisition data or transaction records
To remain compliant, use apps like CoinTracker or Koinly. These tools help in tracking, categorizing, and exporting your crypto transaction history according to Indian tax norms.
Owner & Founding Background of the Crypto Tax Policy in India
The official framework for Tax On Crypto In India was introduced by the Ministry of Finance in the Union Budget 2022. This was led by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, and the rules are enforced by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) and the Income Tax Department.
While crypto is still not legal tender in India, the tax policy officially recognized its existence and brought it under a structured financial framework. This move was seen as a way to monitor crypto activity without banning it outright.
How to File Crypto Taxes in India
Follow this step-by-step process to file taxes under the Tax On Crypto In India regulations:
- Gather transaction data from all exchanges and wallets
- Calculate total gains or losses on each asset
- Deduct any TDS already collected and visible in Form 26AS
- Under the Tax On Crypto In India framework, gains from crypto should be reported as “Income from Other Sources” in ITR-2 or ITR-3.
- Pay the 30% tax along with cess and surcharge
- Keep records for 6 years for future audits
Consider using a crypto tax filing service like ClearTax Crypto to automate reporting.
TDS Compliance for Traders and Exchanges
The 1% TDS under Tax On Crypto In India applies per transaction. This means it applies even when there is no net gain. Centralized exchanges like CoinDCX and WazirX handle TDS automatically, deducting it during trade execution.
For off-chain or decentralized transactions, the responsibility to deduct and deposit TDS lies with the individual. Use Form 26Q to file the deducted amount. Traders using DEX platforms like Uniswap or PancakeSwap must maintain full transparency and record-keeping for audit safety.
Legal Status: Is Crypto Banned in India?
As of now, crypto is not banned in India, but it is not recognized as legal tender either. It operates in a regulated gray area. However, the introduction of the Tax On Crypto In India shows that the government is not looking to ban crypto but to monitor and regulate it.
The Reserve Bank of India remains skeptical and continues to issue warnings about the volatility and financial risks associated with crypto investments.
Future Outlook for Crypto Taxation in India
The government is expected to bring more clarity through the upcoming Digital India Act. This legislation may introduce:
- Streamlined definitions for VDAs
- Slab-based tax rates for retail investors
- Clarifications on loss offsets and staking rewards
- Harmonization with global crypto tax standards
Stakeholders in the Indian crypto space are hoping for a more balanced tax structure that encourages innovation and investor participation.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the Tax On Crypto In India is essential for anyone participating in the crypto economy. The 30% tax and 1% TDS are strict, but they also bring legitimacy to the ecosystem. Staying compliant with crypto tax regulations helps you avoid penalties and keeps your investments secure.
Whether you’re holding Bitcoin long-term, minting NFTs, or actively trading altcoins, make sure you’re on top of your tax obligations. Smart tax planning can go a long way in maximizing your crypto profits in India.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is crypto taxable in India?
Yes, cryptocurrency is taxable in India. As per the Union Budget 2022, income from the transfer of virtual digital assets (VDAs) such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and NFTs is taxed at a flat 30% rate. Additionally, a 1% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) applies to crypto transactions exceeding ₹10,000 in a financial year.
How to file crypto taxes in India?
To file crypto taxes in India, report your crypto income under the “Income from Other Sources” section of ITR-2 or ITR-3. You must maintain detailed transaction records, calculate capital gains or business income, include TDS already paid (visible in Form 26AS), and pay the 30% tax along with applicable surcharge and cess.
Do I need to pay tax if I only hold crypto?
No, you do not need to pay tax if you are only holding crypto and have not sold, transferred, or exchanged it. Tax is applicable only when a taxable event occurs, such as selling, trading, or converting crypto into fiat or another crypto asset.

I work as a content writer in the blockchain and cryptocurrency domain. I have a keen interest in exploring the world of digital assets, Web3, and emerging crypto technologies. My goal is to provide readers with easy-to-understand, engaging, and trustworthy insights, helping them stay informed and confident in the rapidly evolving world of crypto and blockchain.










