
Gas Fees The Brutal Truth Behind Crypto Transactions
Gas Fees: The Brutal Truth Behind Crypto Transactions. In the evolving world of blockchain and digital assets, Gas Fees have become a central talking point. Whether you’re transferring tokens, minting NFTs, or using DeFi applications, gas fees affect every transaction. Understanding what they are and how to minimize them is essential for any crypto user.
What Is Gas Fees?
Transaction charges, commonly known as gas fees, are essential payments required to validate and execute actions on a blockchain network. Primarily associated with Ethereum, gas fees are paid in the network’s native cryptocurrency (Like ETH) and serve as compensation to miners or validators for the computational work they perform.
Each transaction, whether simple or complex, requires computational resources. The complexity of an operation directly influences the amount of gas needed, more intricate actions demand higher gas consumption. Think of gas as fuel; without it, blockchain operations can’t move forward.

Types of Gas Fees
Gas fees can vary depending on several factors. The main types include:
- Base Fee: refers to a dynamically adjusted charge that fluctuates depending on the level of congestion or activity within the blockchain network at a given time. Introduced via Ethereum’s EIP-1559 upgrade, this fee is burned instead of being paid to miners.
- Priority Fee (Tip): An optional amount users can add to speed up processing by incentivizing miners to prioritize their transactions.
- Max Fee: It represents the maximum amount a user is prepared to spend on a transaction. If the actual network fee ends up being lower, the unused portion is automatically refunded to the user.
Understanding these types helps you better estimate costs and avoid failed or delayed transactions.
Why Do Companies Charge or Subsidize Gas Fees?
Companies and platforms may charge users gas fees directly or subsidize them to enhance the user experience. For example, blockchain games or decentralized exchanges might absorb these costs to encourage user adoption. However, in most cases, users are responsible for paying their own Gas Fees.
Projects that rely on frequent transactions, such as NFT platforms or DeFi protocols, might choose to offset gas fee to lower barriers to entry and improve user retention.
How to Qualify for Gas-Free Transactions
Some projects offer gas-free or subsidized transactions under specific conditions:
- First-time User Promotions: Platforms might waive gas fee for new users as an onboarding strategy.
- Holding Specific Tokens: Holding governance or utility tokens may grant access to reduced fees.
- Layer 2 Participation: Some Layer 2 solutions offer nearly gas-free transactions for those using their network.
Look for partnerships or promotional campaigns that specifically advertise gas-free interactions.
Benefits of Paying Gas Fees
Though often seen as a burden, gas fee offer several benefits:
- Security: They prevent spam and protect the network from overload.
- Incentivization: They reward miners and validators, ensuring the blockchain operates smoothly.
- Network Stability: Fees help regulate demand and promote efficient resource use.
Ultimately, gas fees are essential to keeping decentralized ecosystems functional and secure.
Risks and Precautions
Gas fees come with notable risks and challenges:
- High Costs During Peak Times: When the network is congested, gas fees can spike dramatically.
- Transaction Failure: If you underpay, your transaction may fail but still cost gas.
- Scams and Exploits: Some malicious dApps trick users into approving expensive or repeated transactions.
Always double-check transaction details, use trusted wallets, and monitor current gas rates before proceeding.
Where to Find Legitimate Platforms with Reasonable Gas Fees
Legitimate platforms with optimized Gas Fees include:
- Layer 2 Networks: Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync offer dramatically reduced gas costs.
- Gas Fee Aggregators: Platforms that compare transaction costs across blockchains help users find the best rates.
- Wallets with Built-in Estimators: Trust Wallet and MetaMask often include real-time gas estimators and suggestions.
Use platforms known for transparency and user-centric features to avoid overpaying.
Best Strategies to Maximize Efficiency and Minimize Gas Fees
To make the most of your blockchain interactions, consider these strategies:
- Use Off-Peak Hours: Gas fees are usually lower late at night or on weekends when the network is less congested.
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: These reduce costs and improve transaction speeds.
- Set Custom Fees Wisely: Most wallets allow you to set the max gas price—optimize it based on urgency.
- Batch Transactions: Some platforms allow you to group multiple actions in a single transaction.
Staying updated with gas tracking tools can save you significant amounts over time.
Comparison Table: Ethereum vs. Layer 2 Networks
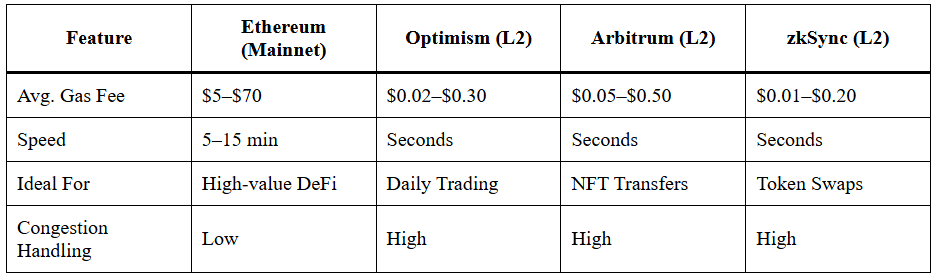
Layer 2 networks clearly offer superior performance and cost-effectiveness, especially for frequent transactions.
Tax Implications of Gas Fees
Gas fees can have various tax implications depending on your region:

- Capital Gains Tax Adjustments: When purchasing a digital asset, the gas fee incurred during the transaction can be included in the asset’s cost basis, potentially reducing future taxable gains upon its sale.
- Deductible Expenses: Active traders and businesses may deduct gas fees as operational expenses.
- Claiming Failed Transaction Fees: In some jurisdictions, even failed gas fees may be claimable.
Always consult a tax advisor familiar with crypto to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Future Outlook for Gas Fees
The future of Gas Fees is evolving rapidly. Ethereum’s move toward scalability through sharding and its transition to proof-of-stake is already improving fee predictability. Meanwhile, more projects are integrating Layer 2 networks, reducing fees and improving transaction times.
Additionally, newer blockchains like Solana and Avalanche are redefining fee models by offering ultra-low-cost transactions. These innovations may eventually normalize affordable, seamless on-chain interactions for all.
As developers continue to innovate and users demand cost efficiency, the crypto industry is steadily working toward a low-fee or fee-optional future.
Conclusion
Gas Fees are an unavoidable yet essential part of the blockchain landscape. While they can be frustrating, they play a crucial role in ensuring security, validating transactions, and maintaining network integrity. By understanding their structure, benefits, risks, and future, users can better navigate the crypto world. Through strategic actions like using Layer 2 networks, timing transactions, and staying informed, you can significantly reduce your gas costs and enjoy a more efficient blockchain experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are transaction fees in crypto?
Transaction fees in crypto are costs users pay to process operations on a blockchain. These fees are used to compensate miners or validators and ensure the network runs securely and efficiently.
2. Why are Ethereum transaction costs sometimes high?
Ethereum fees rise when network demand surges. Activities like DeFi trading, NFT minting, or high transaction volumes cause congestion, leading to increased fees. Layer 2 solutions are often used to address this issue.
3. How can users lower their transaction costs?
To reduce costs, users can transact during off-peak hours, use Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum or Optimism, fine-tune gas settings in their wallet, and batch multiple actions into a single transaction.
I work as a content writer in the blockchain and cryptocurrency domain. I have a keen interest in exploring the world of digital assets, Web3, and emerging crypto technologies. My goal is to provide readers with easy-to-understand, engaging, and trustworthy insights, helping them stay informed and confident in the rapidly evolving world of crypto and blockchain.





