
The internet is going through a major transformation. At the center of this change is decentralization, a powerful concept that gives control back to users instead of corporations or governments. Whether it’s how we manage money, vote on decisions, or build apps, decentralization is changing everything.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll break down what decentralization means, why it’s important, and how it’s used in tools like DeFi (Decentralized Finance), smart contracts, DApps, and DAOs.
What Is Decentralization?
Decentralization means that power, control, and decision-making are spread out, rather than being held by one central authority.

In traditional systems:
- A bank controls your money.
- A company owns your data.
- A government manages your identity.
But in decentralized systems:
- No single party is in charge.
- Rules are enforced by transparent code.
- Everyone has equal access and rights.
This is made possible by blockchain technology, a distributed digital ledger where every transaction is verified by a network of computers (nodes). No one can secretly change the data. Everything is visible and secure.
Key Benefits:
- Censorship resistance: Your transactions are immune to interference. No external authority can prevent, modify, or reverse your transactions.
- Transparency: All actions are recorded publicly.
- Security: No single point of failure or control.
- User ownership: You control your money, identity, and assets.
Decentralization is not just a technical shift, it’s a philosophical one. It supports the idea that trust should be built into the system itself, not dependent on companies, banks, or governments.
What Is DeFi (Decentralized Finance)?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance. It’s a set of financial services built on blockchain that lets you:
- Lend and borrow money
- Earn interest on crypto
- Trade tokens
- Use stablecoins
- Insure digital assets
And all of this happens without needing a bank, broker, or financial advisor.
DeFi is typically built on the Ethereum blockchain, using smart contracts to manage the rules of the system.
Example:
If you lend your crypto on a DeFi platform like Compound, a smart contract will automatically:
- Lock your funds
- Pay you interest
- Return your funds when requested
You don’t need to trust a company. You trust the code, which is open for anyone to see.
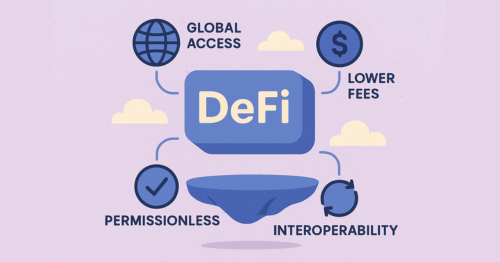
Why DeFi Matters:
- Global Access: Anyone with a phone and internet can join.
- Lower Fees: No middlemen taking cuts.
- Permissionless: No approval needed from banks or governments.
- Interoperability: DeFi platforms can connect and build on each other.
What Can You Do with DeFi?
DeFi is more than just a buzzword. It offers real tools for everyday people. Here are its most common use cases:

1. Lending and Borrowing
Put your crypto to work by offering it as a loan and collecting interest. Or borrow against your crypto without selling it.
- Platforms: Aave, Compound
- How it works: You supply funds to a liquidity pool and earn a percentage from borrowers.
2. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Directly trade different cryptocurrencies without relying on a centralized exchange. No sign-up or personal information required.
- Platforms: Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap
- Why it’s better: You keep control of your funds at all times.
3. Yield Farming and Staking
Earn incentives by committing your crypto to decentralized finance protocols. Some users combine platforms to maximize returns.
- Yield farming: Providing liquidity and earning fees + tokens.
- Staking: Locking coins to support network operations and earn passive income.
4. Stablecoins
Stablecoins mirror the price of real-world money, with most linked to currencies like the US dollar. They help avoid crypto’s price volatility.
- Examples: DAI, USDC, USDT
- Use case: Trading, saving, or sending money globally with stable value.
5. DeFi Insurance
Protect your assets in case a smart contract gets hacked or fails.
- Platforms: Nexus Mutual, InsurAce
- Why it’s useful: DeFi can be risky, so having insurance helps manage that risk.
What Are Smart Contracts?
A Smart Contract is an automated program that runs on the blockchain without human intervention. It runs automatically when the set conditions are met, no middleman, no delay.

Real-Life Example:
A vending machine:
- Insert money → choose product → product is delivered.
- No shopkeeper needed.
Smart contracts work the same way:
- “If you send 1 ETH, the contract will send back 100 tokens.”
- No person needed to approve, track, or confirm.
Features:
- Automated: Executes without manual input.
- Immutable: Once deployed, can’t be changed.
- Transparent: Code is publicly visible.
- Trustless: No middlemen or trust required, everything runs purely on code.
They are the foundation of all DeFi apps, DApps, and DAOs.
What Are DApps (Decentralized Applications)?
DApps are apps built on blockchains, powered by smart contracts. Unlike regular apps:
- They are not owned or controlled by any single company.
- They operate 24/7.
- Their data and actions are stored on a public blockchain.
Key Characteristics:
- Open-source: Anyone can view or improve the code.
- Tokenized: Many DApps use tokens to reward users or enable features.
- Permissionless: Anyone can use or build on top of it.
Examples:
- Uniswap – Swap tokens instantly
- OpenSea – Buy and sell NFTs
- Lens Protocol – Decentralized social media
DApps are creating new ecosystems, social networks, games, and marketplaces. Where users own and control their experience.
What Is a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)?
A DAO is a decentralized organization governed by smart contracts rather than traditional leadership like managers or CEOs.

DAO members hold governance tokens that allow them to vote on key decisions.
They can vote on:
- How funds are spent
- Which projects to support
- Which updates or changes to make
Key Features:
- Democratic: One token = one vote (in most cases)
- Transparent: All decisions are recorded on-chain.
- Borderless: Anyone, anywhere, can participate.
Real Examples:
- MakerDAO: Runs the DAI stablecoin.
- Uniswap DAO: Decides on protocol upgrades.
- Gitcoin DAO: Funds public goods and developers.
DAOs are changing how communities are formed and managed, giving every member a real say in how things work.
Why Does Decentralization Matter?
Centralized systems are vulnerable:
- A single individual or company can make poor choices that affect everyone.
- Data can be stolen, manipulated, or deleted.
- Systems can break down, be compromised by hackers, or be taken offline unexpectedly.
Decentralized systems fix this:
- No single point of failure
- Rules are enforced by code, not people
- Everyone has equal access
In short, decentralization makes the internet fairer, safer, and more empowering for individuals.
How to Get Started
It’s easy to explore decentralization step by step:
- Set up a crypto wallet: Use MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Coinbase Wallet.
- Buy a small amount of crypto: Ethereum is a good starting point.
- Visit a DApp: Try Uniswap, Lens Protocol, or Mirror.xyz.
- Join a DAO: Visit Snapshot.org to find DAOs and vote.
Start small. Ask questions. Learn by doing.
Final Thoughts
Decentralization is not just a trend, it’s the future. It’s about putting control into the hands of people, not platforms. Whether it’s finance, governance, identity, or creativity, decentralized systems offer an alternative that is transparent, fair, and user-driven.
As the space grows, so do your opportunities to participate. You don’t need to be a developer or investor, just curious and open to learning.
Welcome to the decentralized world. The future is yours to shape.









