
Welcome to the Cryptocurrency Deep Dive, your ultimate resource for mastering the digital money revolution. Whether you’re new to Bitcoin, eager to explore Ethereum, or simply curious about how blockchain technology powers it all, this beginner-friendly guide walks you through every essential concept, step by step.
From the origins of money to the mechanics of decentralized networks, from how to store your crypto securely to understanding real-world use cases, this guide is designed to simplify complex topics and help you make informed decisions in the world of cryptocurrency.
Get ready to unlock the future of finance, one block at a time.
FOUNDATIONS OF CRYPTOCURRENCY

Understanding Money and Cryptocurrency
Before diving into cryptocurrency, it’s crucial to understand what money really is. Money isn’t just paper notes or coins, it’s a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. Traditionally, we’ve relied on centralized authorities like governments and banks to issue and manage money.
Cryptocurrency challenges this model by creating digital money that isn’t controlled by any central entity. Instead, it relies on cryptography, code, and community consensus. It’s borderless, permissionless, and, in many cases, deflationary.
- Medium of Exchange: Traditional money (INR, USD, EUR) helps people trade goods and services. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and USDT are accepted by thousands of businesses globally, including Shopify stores, travel websites, and freelancers.
- Store of Value: Inflation erodes fiat value. And ₹100 in 2000 could buy far more than ₹100 today. In contrast, Bitcoin’s limited supply of 21 million has made it a hedge against inflation. BTC grew from $0.003 in 2010 to over $60,000+ at peak.
- Unit of Account: Cryptos are used to denominate prices on NFT marketplaces (e.g., ETH on OpenSea), in DeFi (e.g., stablecoins like USDC on Aave), and in DAOs (e.g., governance votes using tokens).
Think of crypto as the evolution of money, from gold to paper to digital.
History of Cryptocurrency
The roots of cryptocurrency go back decades. In the 1980s and 1990s, cypherpunks began experimenting with digital cash systems. But it wasn’t until 2009 that cryptocurrency truly came alive with the birth of Bitcoin, created by the anonymous figure Satoshi Nakamoto.
Bitcoin was launched as a response to the 2009 financial crisis, with the vision of giving people control over their money. It introduced the world to Blockchain Technology, a public ledger that records transactions transparently and securely.
Since then, thousands of cryptocurrencies have emerged, each aiming to solve different problems, from Smart Contracts (Ethereum) to privacy (Monero) and scalability (Solana).
- Early Concepts: In 1983, David Chaum introduced DigiCash, which used blind signatures for digital payments. While innovative, it required a central server, making it vulnerable.
- Bitcoin Launch (2009): In response to the 2008 recession and bank bailouts, Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin to empower individuals with self-custodial money.
- Crypto Evolution: Ethereum (2015) added programmability. DeFi summer (2020) brought yield farming. NFTs (2021) disrupted art. Since 2022, Web3 and the Metaverse have started changing how we own things and show who we are online.
The Mechanics of Cryptocurrency: Blockchain
Every cryptocurrency runs on a blockchain, which is a secure, unchangeable digital record that isn’t controlled by one person or company. It records every transaction in “blocks” that are cryptographically linked to one another, forming a chain.
Here’s how it works:
- Decentralized Network: Thousands of computers (nodes) verify and store the blockchain.
- Transparency: Anyone can view the transaction history.
- Security: Data is encrypted and nearly impossible to alter.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Systems like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure everyone agrees on the state of the network.
- Distributed Ledger: Blockchain stores a copy of all transactions across thousands of nodes. If one node fails or is hacked, the data remains safe and validated by others.
- Consensus Mechanism:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin. Miners solve puzzles to secure the network, consuming high energy (~91 TWh/year globally).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Ethereum 2.0 and Solana use a system called Proof of Stake, where validators are chosen at random based on the amount of tokens they’ve locked in. It’s faster and better for the environment than older methods.
- Security via Hashing: SHA-256 hash in Bitcoin ensures that changing a transaction requires re-mining every subsequent block, mathematically impossible for any attacker.
In simple terms, blockchain allows people to trust the system without needing to trust each other, a foundational shift in how we think about value exchange
Cryptocurrency Use Cases
Cryptocurrency is not just about trading coins for profit. It’s a tool for real-world innovation. Here are some powerful ways cryptocurrency and blockchain are being used today:
- Cross-Border Payments: Sending money across countries using cryptocurrencies like XRP or USDT takes just seconds and costs less than 1%, compared to traditional banks that can take 3–5 days and charge 5–10% in fees.
- Smart Contracts: Used in DAOs, DeFi, and gaming. E.g., Uniswap v3 executes trades without intermediaries. Ethereum-based Smart Contracts hold over $60 billion in DeFi assets (2024).
- Stablecoins: Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and DAI offer fiat-pegged stability. They power daily trading volumes over $80 billion across platforms.
- DeFi Protocols: Compound, Aave, MakerDAO allow decentralized lending/borrowing with smart contract transparency. Aave alone has over $8B TVL (Total Value Locked).
- NFTs and Gaming: Games like Axie Infinity (once valued at $4B) pay users to play. NFTs generated $40B in revenue in 2021 alone.
As adoption grows, new use cases continue to emerge, from decentralized social media to gaming and even identity verification.
GETTING STARTED WITH CRYPTO

Cryptocurrency Wallets
A crypto wallet lets you safely store, send, and receive digital money like Bitcoin or Ethereum. It doesn’t actually hold coins like a physical wallet, instead, it stores private and public keys that allow you to access and control your assets on the blockchain.
- Hot Wallets: Web/mobile wallets (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet) are user-friendly and support dApps. MetaMask has over 30M+ active users. But they are online, making them vulnerable to phishing and hacks.
- Cold Wallets: Devices like Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T store your private keys offline, keeping your crypto safe from online hacks. When used correctly, hardware wallets have never been hacked. Ideal for long-term HODLers and investors with large funds.
- Seed Phrase Importance: Wallets use a 12–24 word recovery phrase. Losing it = losing funds permanently. Never share or store it online.
Key Tip: “Not your keys, not your crypto.” Always back up your wallet and store your seed phrase securely. Anyone who gets your private keys can take control of your crypto and move your funds.
Read All About: Crypto Wallet: Cold Vs Hot Wallet
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized exchanges are websites or apps that help people buy and sell crypto by acting as the middleman. They offer user-friendly interfaces and high liquidity, making them ideal for beginners.
- Ease of Access: CEXs like Binance (120M+ users) and Coinbase (publicly listed, NASDAQ) offer fast onboarding, UPI support, and intuitive UI.
- High Liquidity: Binance processes $76B+ daily volume. This means smaller spreads, deeper order books, and faster trade execution.
- Drawback: Exchanges control your funds (custodial wallets). If an exchange is hacked (e.g., Mt. Gox lost 850,000 BTC in 2014), users risk losing assets.
Key Features:
- Easy KYC (Know Your Customer) onboarding
- Fiat-to-crypto options (like INR to BTC)
- High-speed order matching
- Customer support and mobile apps
Risk to Know:
When you store assets on CEXs, you’re trusting the platform to manage your crypto. If a centralized exchange gets hacked or goes offline, you could lose access to your money. That’s why many users move assets to personal wallets after trading.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges allow you to trade crypto directly from your wallet, without any central authority or account creation.
- Non-Custodial: Wallets like MetaMask connect directly. Your private keys never leave your device, “Not your keys, not your coins” applies here.
- Liquidity Pools: Protocols like Uniswap and SushiSwap use AMMs (Automated Market Makers) instead of order books. Users provide liquidity and earn fees/yield in return.
- Risks: Impermanent loss, front-running (MEV bots), and smart contract bugs, especially in unaudited platforms.
How DEXs Work:
They use smart contracts to match and execute trades, meaning no middleman holds your funds. You’re in full control.
Advantages:
- Full ownership of your funds
- No need for KYC or sign-ups
- Often access to newer, smaller tokens early
Keep in Mind:
- Slightly complex for newcomers
- Network fees can be high depending on the blockchain
- No customer support or recovery options if mistakes are made
How to Buy and Sell Crypto
Buying crypto might seem complicated at first, but it’s easier than ever today. Most users start by creating an account on a centralized exchange (CEX) and purchasing with fiat currency (like INR, USD, or EUR).
How to Buy Crypto in 5 Simple Steps:
- Choose a trusted exchange (e.g., Binance, Coinbase, WazirX)
- Complete KYC verification
- Add payment method (bank transfer, UPI, card)
- Buy crypto like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or USDT
- Store in a wallet (either leave it on the exchange or transfer to a personal wallet)
- Example Process (India):
- Fees: CEXs charge ~0.1–0.5% per trade; gas fees on Ethereum range from $1–$50 depending on network load.
- Timing Matters: Buying during low network congestion (e.g., weekends) can reduce gas and slippage.
Popular Payment Options in India:
- UPI and IMPS
- Net Banking
- Debit/Credit Cards (on select platforms)
Tip for First-Timers:
Start with a small amount and get familiar with how transactions, confirmations, and fees work before investing larger sums.
Risk Management in Crypto Investment
With crypto, you’re in complete control of your money, but you’re also fully responsible for keeping it safe.
- Diversification Example: Portfolio could be 40% BTC, 30% ETH, 15% DeFi tokens, 10% stablecoins, 5% NFTs, based on risk appetite.
- Stop-Loss Strategy: On a 10% dip, auto-sell triggers, protecting from deeper crashes. CEXs like Binance or KuCoin support this.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): Investing ₹1,000 weekly into BTC smooths out volatility vs lump-sum investing.
- FOMO & Hype: Avoid emotional trading. Coins pumped on social media (like Dogecoin) may crash 80–90% quickly.
Red Flags to Avoid:
- “Too good to be true” investment schemes
- Random DMs or giveaways asking for wallet details
- Fake customer support pages on social media
By following strong security practices, you’ll protect your assets and avoid common beginner mistakes.
BITCOIN DEEP DIVE

The Bitcoin Whitepaper
The foundation of Bitcoin begins with the Bitcoin Whitepaper.
Titled: “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”,
Bitcoin was first introduced in a whitepaper published by Satoshi Nakamoto on October 31, 2008.published by Satoshi Nakamoto on October 31, 2008.
This 9-page document outlined a bold solution to digital payments without intermediaries. It introduced blockchain, proof-of-work, and a new trustless monetary system that could function without central banks.
- Release Date: Oct 31, 2008.
- Problem Solved: Double-spending without a central party.
- Notable Quote: “What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust.”
- Impact: It sparked a $2 trillion+ crypto industry and inspired thousands of decentralized projects.
Key Highlights from the Whitepaper:
- Peer-to-peer transactions with no need for a trusted third party (bank, PayPal, etc.)
- A solution to the double-spending problem using decentralized consensus
- It works by recording transactions in blocks, which are securely connected using cryptography to form a chain.
- Mining was introduced as a way to confirm transactions and create new coins in the network.
Bitcoin’s UTXO Model
Bitcoin uses something called the UTXO model (Unspent Transaction Output), which is different from how traditional bank accounts work.
In a nutshell, your Bitcoin balance isn’t stored as one number in a wallet, but rather as multiple unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs) that are associated with your address.
- Each BTC Transaction creates “inputs” and “outputs.”
- Unspent Outputs (UTXOs) = actual spendable balance.
- Example: If Alice receives 0.5 BTC and sends 0.2 BTC to Bob, she gets 0.3 BTC as a new UTXO.
- Benefits: Efficient validation, privacy (pseudonymous addresses), and minimized double-spending risk.
How it works:
- When you receive Bitcoin, it’s saved as small chunks called UTXOs, which stand for Unspent Transaction Outputs.
- When you spend Bitcoin, your wallet gathers enough UTXOs to match the amount and creates a new transaction.
- Any leftover Bitcoin from a transaction is sent back to your wallet as a new UTXO, like getting change after a purchase.
UTXO vs Account Model:
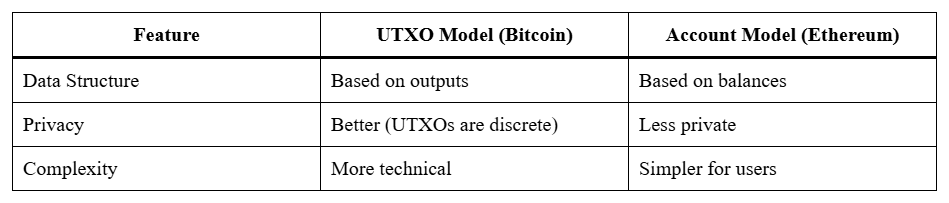
The UTXO model enhances privacy, traceability, and security, though it may seem more technical to beginners.
Understanding Bitcoin Tokenomics
One of the best things about Bitcoin is how its money system works. Unlike regular money, Bitcoin has a limited supply, is fully transparent, and follows strict rules that can’t be changed easily.
- Max Supply: 21 million BTC. ~19.7M BTC mined as of July 2025.
- Halvings: Every 210,000 blocks (~4 years). Next halving expected in 2028 will reduce block reward to 1.5625 BTC.
- Lost Coins: An estimated 3–4 million BTC are lost forever (due to lost keys), making actual supply more scarce.
Distribution via Mining:
- New bitcoins are created through a process called Proof of Work (PoW) mining, where powerful computers solve complex puzzles to confirm transactions and earn rewards.
- Miners are incentivized with: Block rewards (new BTC) and Transaction fees
Economic Implications:
- As supply decreases and demand grows, price tends to increase (supply-demand economics)
- Encourages long-term holding (HODLing)
- Influences the development of Layer 2 solutions like the Lightning Network to scale transactions
Bitcoin’s tokenomics is predictable and transparent, unlike central bank policies that can change based on politics or crises.
ETHEREUM DEEP DIVE

The Ethereum Whitepaper
Ethereum was first introduced through a whitepaper published in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a young programmer who envisioned a platform that could do more than just send digital currency.
In the whitepaper titled “Ethereum: A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform,” Buterin proposed a Turing-complete blockchain, one that could run complex applications (smart contracts) with global consensus, without intermediaries.
Key Concepts Introduced:
- A general-purpose blockchain that can be programmed
- Smart contracts that execute automatically based on code
- The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to support decentralized computation
- A native token (Ether) to pay for computation (gas fees)
Ethereum aimed to become the decentralized app store of the blockchain world, and today, it powers thousands of applications across finance, gaming, identity, and more.
Ethereum’s Account Model
Unlike Bitcoin’s UTXO system, Ethereum uses an account-based model, more intuitive and familiar to traditional banking users.
Ethereum has two types of accounts: one for regular users (externally owned accounts) and one for smart contracts (contract accounts):
- Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs):
- Controlled by a private key
- Used by individuals (e.g., MetaMask users)
- Can send ETH and interact with contracts
- Contract Accounts:
- Controlled by code (smart contracts)
- Execute when called by EOAs or other contracts
- Can store ETH and data, but don’t initiate transactions themselves
How It Works:
- An Ethereum account’s balance changes each time a transaction is made, it’s stored and updated on the blockchain.
- Each account has:
- Nonce (transaction count to prevent replay)
- ETH balance
- (for contracts) Contract code and storage
The account model is simpler for developers but introduces unique considerations around gas optimization, state management, and security.
Understanding Ethereum Tokenomics
Ethereum’s tokenomics has undergone major changes, especially with the transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) and the implementation of EIP-1559.
Key Components of Ethereum Tokenomics:
Native Token : ETH
- Used to pay for gas (network computation)
- Required for staking and network security
- Deflationary due to EIP-1559 (more below)
EIP-1559 and Fee Burn
Launched in August 2021, EIP-1559 updated how Ethereum fees work by burning a portion of the fees and making costs more predictable:
- Every Ethereum transaction includes a base fee that is burned, meaning it’s permanently removed from the supply.
- An optional tip (priority fee) goes to validators
- This means ETH is regularly burned, making it potentially deflationary
Transition to Proof of Stake (PoS)
In September 2022, Ethereum completed The Merge, moving from Proof of Work to a greener system called Proof of Stake, which uses much less energy.
- No more energy-intensive mining
- Validators secure the network by staking ETH
- Stakers are rewarded with newly issued ETH + transaction tips
Supply Dynamics:
- No hard cap like Bitcoin
- Thanks to EIP-1559 and staking, the amount of new ETH being created has dropped a lot.
- ETH may become net deflationary if burn exceeds issuance
Economic Incentives:
- To use the Ethereum network, users pay a small fee in ETH called gas.
- Developers build DApps that rely on ETH for operations
- Validators earn ETH for securing the chain
Ethereum’s tokenomics create sustainable demand, real utility, and long-term alignment between users, developers, and validators.
Emerging Trends and the Future of Cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency is no longer just about Bitcoin and Ethereum. As the ecosystem matures, we’re witnessing an explosion of innovation, adoption, and integration across finance, technology, and society. Let’s explore the key trends shaping the next decade of crypto.
Mass Adoption of Crypto in Everyday Life
From payments and gaming to digital identity and ticketing, cryptocurrencies are slowly integrating into real-world experiences.
- Big companies like PayPal and Shopify now let people pay with cryptocurrency.
- Countries like El Salvador and CAR have adopted Bitcoin as legal tender.
- CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies) are in testing or pilot phases globally.
What it means: Crypto will become more accessible to the average user, often without them even knowing they’re using blockchain in the background.
Rise of Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
As Ethereum has become more popular, the network has gotten crowded, causing slow transactions and high gas fees. Enter Layer 2 solutions, protocols that sit on top of Ethereum to process transactions faster and cheaper.
- Rollups (Optimistic & ZK): Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync
- Sidechains: Polygon (Matic)
- App-specific chains: Base (by Coinbase), StarkNet
What it means: Faster DApps, lower fees, and improved user experience, all without compromising Ethereum’s security.
Real-World Asset Tokenization (RWA)
Everything from real estate to bonds, art, and stocks is being tokenized and brought on-chain.
- Projects like Ondo Finance, Backed Finance, and Centrifuge are leading the charge.
- BlackRock, JPMorgan, and HSBC are exploring tokenized securities.
What it means: Blockchain isn’t just for crypto anymore, traditional finance (TradFi) is getting a DeFi makeover.
Web3 Gaming and the Metaverse
Gaming and blockchain are coming together, creating play-to-earn games, digital items you truly own, and more interactive experiences.
- Platforms like The Sandbox, Axie Infinity, and Decentraland are creating digital economies.
- NFTs in games let players truly own their in-game items and trade them with others, just like real-world collectibles.
What it means: Players are no longer just users, they’re participants, investors, and builders in digital worlds.
Institutional Investment and Regulation
Institutions are no longer ignoring crypto, they’re entering the space with caution, compliance, and capital.
- Spot Bitcoin ETFs and ETH futures have gained regulatory traction.
- Regulatory clarity is emerging in the US, EU, and Asia.
- Regular banks are now creating services to safely store and trade cryptocurrencies for their customers.
What it means: Institutional capital brings legitimacy and scale, but also tighter regulation and surveillance.
Privacy, Security & Self-Custody
With rising awareness of data breaches, surveillance, and hacks, there’s growing demand for:
- Privacy coins (Monero, Zcash)
- Decentralized Identity (DID) protocols
- Self-custody wallets like Ledger, Trezor, and multisig solutions
What it means: Users want control, not just over money, but also over identity and personal data.
The Future Is Multi-Chain
No single blockchain will rule them all. The future is interoperable, with bridges, cross-chain swaps, and ecosystems working together.
- Projects like Cosmos (IBC) and Polkadot (parachains) are enabling blockchain interoperability.
- Cross-chain DeFi is becoming a norm via aggregators like 1inch and ThorChain.
What it means: Users won’t care what chain they’re on, they’ll simply use apps that work seamlessly.
The Road Ahead
The next few years in crypto will be shaped by:
- Improved user experience (UX)
- Scalable infrastructure
- Regulatory maturity
- Massive developer growth
- Real-world integration
Cryptocurrency is not just an asset class. It’s the infrastructure for a more open, programmable, and decentralized digital world.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency isn’t a trend, it’s a technological evolution. Whether you’re here to invest, innovate, or learn, this guide equips you with the knowledge to start confidently.
Stay safe, self-custody your assets, and keep learning. Web3 rewards the informed.









