
Blockchain Deep Dive: Unlocking Complex Concepts Simply. Explore scaling, consensus, Web3, and tokenomics in our ultimate deep dive guide. Project Deep Dives presents a comprehensive exploration into blockchain technology. This guide breaks down core components, advanced scaling solutions, and the future potential of Web3, all explained in a professional yet digestible format. Welcome to your ultimate Blockchain Deep Dive.
Core Building Blocks of Blockchain
What’s in a Block?
Every blockchain is built from units called blocks, digital containers that store data. A typical block contains:
- Block Header: The header contains metadata such as timestamp, version, and a reference to the previous block’s hash. It ensures chronological ordering and connects the current block to the chain, forming a verifiable sequence.
- Merkle Root: A single cryptographic hash that efficiently summarizes and verifies all transactions within a block, ensuring data integrity and enabling quick validation of individual transactions. It allows efficient and secure verification of the contents without needing to examine each transaction.
- Nonce & Hash: A nonce is a random value used by miners to solve cryptographic puzzles. The resulting hash must meet network difficulty, ensuring proof of computational work before a block is accepted.
These blocks are immutable once added, making blockchain a secure, decentralized ledger.
How Are Transactions Authenticated?
Blockchain transactions use public-key cryptography. Each participant uses a private key to securely sign transactions and a matching public key to receive funds or encrypted information from others. Once a transaction is signed:
- Private Key Signatures: Each participant signs transactions using their private key, generating a unique digital signature that proves ownership, ensures authenticity, and authorizes the transaction on the blockchain.
- Public Key Verification: The blockchain network uses the sender’s public key to verify the digital signature, ensuring that the transaction was indeed authorized by the rightful owner and has not been tampered with. If verified, it ensures that the transaction wasn’t altered and came from the rightful user.
- Consensus-Based Inclusion: Once verified, transactions are validated through consensus before being added to the next block. This decentralized validation adds a layer of trust and prevents fraudulent activities.
This ensures trustless, secure, and tamper-proof records.
Read All About: Crypto Wallet And Authentication
Building Consensus Within Blockchain Networks
Consensus mechanisms prevent fraud and double-spending. Major types include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems. This mechanism ensures high security but requires immense computational power and energy.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): A consensus mechanism where validators are selected to create new blocks and confirm transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked, promoting energy efficiency and network security.
Real All About: Proof Of Stack (PoS) - Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Token holders vote to elect a few trusted validators. This speeds up consensus but sacrifices a bit of decentralization for performance.
Each method has trade-offs in speed, decentralization, and energy efficiency, a critical part of this Blockchain Deep Dive.
Exploring the Blockchain Spectrum
Blockchain types include:
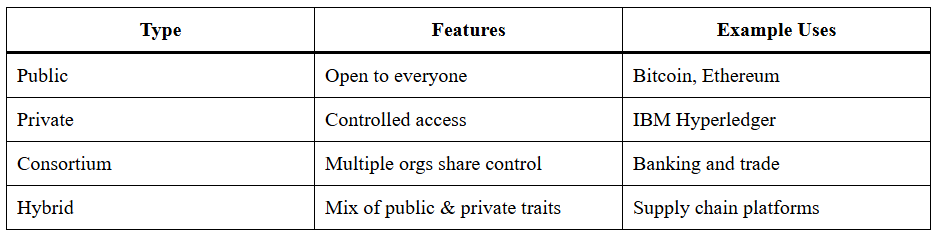
Understanding the spectrum helps define use case alignment across industries.
Navigating Advanced Blockchain Challenges

Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
Interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and operate seamlessly with one another, enabling greater connectivity and functionality across ecosystems. It’s vital for cross-chain functionality and ecosystem collaboration.
Solutions include:
- Wrapped Tokens: Digital assets that represent the value of a cryptocurrency from one blockchain on a different blockchain, such as wBTC, which mirrors Bitcoin on the Ethereum network, enabling cross-chain asset utilization and liquidity. This allows liquidity to flow between chains without compromising asset ownership.
Read All About: Wrapped Token: Benefits And Key Risk - Bridges: Act as gateways that enable asset and data transfers between two distinct blockchain networks. However, they need rigorous security due to their vulnerability to attacks.
- Interchain Protocols: Frameworks like Polkadot and Cosmos allow seamless communication between multiple chains. They support decentralized applications that span across platforms.
Effective interoperability unlocks innovation and mass adoption.
The Blockchain Trilemma
Coined by Vitalik Buterin, the Blockchain Trilemma posits that it’s difficult to achieve:
- Decentralization: Ensures no single entity controls the network. However, excessive decentralization can lead to slower transaction speeds, as reaching consensus across a larger, distributed network often requires more time and coordination.
Read All About: Decentralized Finance (Defi) - Security: Protects against attacks and ensures transaction validity. Boosting security often requires centralization or lower throughput.
- Scalability: The capability of a blockchain network to efficiently process a high volume of transactions per second without compromising speed, security, or decentralization. High scalability often leads to compromises in decentralization or security.
Most networks can fully satisfy only two at once. Projects like Ethereum 2.0 and Solana are actively trying to solve this using hybrid solutions and new consensus algorithms.
Blockchain Scaling: On-Chain Solutions
On-chain solutions focus on scaling the base layer by improving the core blockchain protocol itself, enhancing transaction throughput, optimizing consensus mechanisms, and increasing block capacity without relying on external layers:
- Sharding: Divides the network into smaller pieces (shards), each processing its transactions and smart contracts. It reduces the burden on the entire chain and boosts throughput.
- State Channels: A layer 2 solution that allows participants to conduct multiple transactions off-chain, recording only the final outcome on the blockchain—reducing congestion, fees, and latency. This reduces congestion and allows instant transaction finality.
- Adaptive Block Sizes: Increase or decrease block size depending on demand. This flexibility helps manage network load efficiently without compromising performance.
These solutions help reduce congestion on the mainnet and significantly enhance transaction throughput across the network.These reduce the load on the mainnet and improve transaction throughput.
Blockchain Scaling: Off-Chain Solutions
Off-chain solutions use secondary layers:
- Lightning Network: Designed for Bitcoin, it enables fast, low-fee micropayments. It facilitates transactions off-chain and settles them later on the main chain.
- Rollups (ZK and Optimistic): A layer 2 scaling solution that bundles multiple transactions into a single batch, which is then submitted to the main chain, reducing fees and improving scalability without compromising security.
- Sidechains: Independent blockchains connected to the main chain via a two-way peg. They allow experimentation and scalability without affecting the main network.
These innovations allow blockchain to scale while maintaining decentralization and security.
Web3 and Decentralized Empowerment

Blockchain, Web3, and Data Ownership
Web3 is the next evolution of the internet, leveraging blockchain technology to enable decentralized applications, user ownership, and greater control over data and digital identity. It emphasizes:
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Users own and manage their credentials without relying on centralized platforms. It empowers individuals and reduces the risks of data breaches.
- Decentralized Storage: Platforms like IPFS store data across a distributed network. This prevents censorship and promotes data permanence.
- User-Centric Economy: Individuals earn from their data, content, and participation. Unlike Web2 models, Web3 incentivizes user ownership and control.
In a Web3 world, users control their identities, wallets, and data, a significant shift from centralized platforms.
Web3 Business Models and Tokenomics
Web3 operates on token-driven economies. Key models include:
- Utility Tokens: Provide access to platform functions and services. They’re the fuel behind dApps and incentivize usage within ecosystems. (e.g., UNI for Uniswap).
- Governance Tokens: Tokens that grant holders the right to participate in decision-making processes, such as voting on protocol upgrades, funding proposals, or policy changes within a decentralized network.
- Play-to-Earn Models: Gaming frameworks where users earn blockchain-based tokens or digital assets as rewards for in-game activities, promoting active participation and creating real-world value from gameplay.
Tokenomics shapes project sustainability, user growth, and value creation.
Read All About: Crypto Tokens
Web3 Use Cases and Ecosystems
Web3 spans across industries:
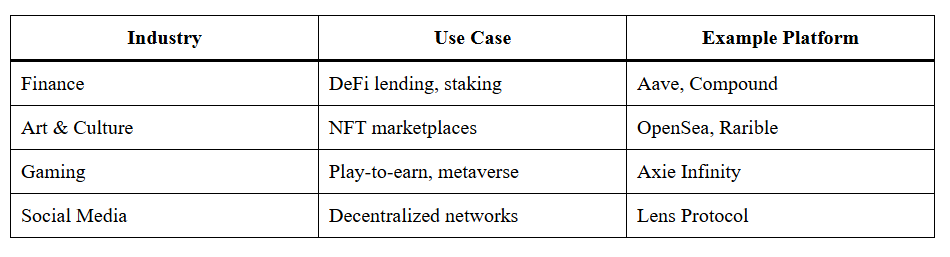
These ecosystems empower communities to build and profit collectively.
Extended Insights from the Blockchain Deep Dive
How Blockchain is Changing Global Finance
The Blockchain Deep Dive wouldn’t be complete without addressing fintech disruption. From remittances to real-time settlements, blockchain slashes transaction costs and increases access.
- CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies): Governments are exploring blockchain-powered fiat.
- Tokenized Assets: Stocks, real estate, and bonds are being digitized for fractional ownership.
This evolution is driving a shift from traditional finance (TradFi) to decentralized finance (DeFi).
Smart Contracts: Automation Without Middlemen
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that power DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and more. Their benefits include:

- Trustless Execution: No intermediaries.
- Transparency: Code is publicly verifiable.
- Automation: Reduces manual processes.
However, vulnerabilities exist. Poor coding or unverified contracts can lead to exploits. Audits and bug bounties are essential precautions.
DAOs and the Rise of Decentralized Governance
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) govern Web3 platforms. DAO tokens grant voting power to users, enabling:
- Community-led decision-making
- Treasury management
- Protocol upgrades
DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) exemplify the transition from traditional centralized hierarchies to bottom-up, community-driven governance models, where decisions are made collectively through transparent, on-chain voting.
Conclusion: The Power of Blockchain Unlocked
This Blockchain Deep Dive demystifies the layers of blockchain technology, from blocks and consensus to tokenomics and beyond. As blockchain matures, it promises a decentralized world where users regain control, businesses innovate transparently, and systems operate without intermediaries.
By understanding the inner workings, real-world applications, and scaling strategies, readers are empowered to engage confidently in the blockchain revolution. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or enthusiast, the knowledge gained here lays the groundwork for meaningful participation in the future of decentralized technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a blockchain and how does it work?
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It works by storing data in blocks that are cryptographically linked to one another, forming an immutable chain. Each transaction is verified by network consensus, ensuring trust without the need for intermediaries.
What are the different types of blockchains?
The main types of blockchains are public, private, consortium, and hybrid.
1. Public blockchains are open and decentralized.
2. Private blockchains are controlled by a single organization.
3. Consortium blockchains are governed by a group.
4. Hybrid blockchains combine features of both public and private systems.
How does blockchain achieve security and transparency?
Blockchain ensures security through cryptographic hashing, decentralization, and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
Transparency is achieved because every transaction is recorded on a public or shared ledger, which can be audited in real-time and is immutable once confirmed.
What is the blockchain trilemma and why is it important?
The blockchain trilemma refers to the challenge of achieving decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously. Most networks excel at only two of these, sacrificing the third. Solving this trilemma is crucial for building scalable, secure, and truly decentralized blockchain systems.
What are the real-world applications of blockchain and Web3?
Blockchain and Web3 are used in diverse sectors such as finance (DeFi), supply chain management, digital identity, healthcare, and gaming.
1. DeFi platforms offer decentralized trading and lending.
2. Web3 apps enable user-owned data and decentralized governance, redefining how businesses and users interact online.









