Proof Of Stake In Blockchain: A Powerful Shift Explained. As the blockchain world evolves, Proof Of Stake In Blockchain is emerging as a game-changing innovation, offering a sustainable, secure, and efficient alternative to the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism.
What Is Proof Of Stake In Blockchain?
Proof Of Stake In Blockchain refers to a consensus mechanism where participants validate transactions and add new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake as collateral. Unlike Proof of Work, which requires high-powered computing hardware and consumes massive energy, PoS relies on economic incentives.
Participants who lock a certain amount of coins, called “stakers” or “validators”, are selected to validate transactions. The more coins staked, the higher the chance of being selected. This method promotes efficiency, reduces energy consumption, and democratizes network participation.
Why Is Proof Of Stake Important?
The importance of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain lies in its ability to address many limitations of Proof of Work, such as high energy costs and centralization of mining power.

Benefits include:
- Energy Efficiency: PoS drastically reduces environmental impact compared to PoW.
- Cost-Effectiveness: No need for specialized mining equipment.
- Security: Misbehaving validators can lose their staked tokens.
- Inclusiveness: More users can participate with smaller amounts of crypto.
As a result, many next-generation blockchains are adopting PoS as their core protocol.
How Does Proof Of Stake Work?
1. Validator Selection
In PoS, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they stake and the duration of the stake. Randomized algorithms and reputation metrics often influence the final selection.
2. Staking Mechanism
Users lock up a fixed amount of crypto as a security deposit. If they validate honestly, they earn rewards. If they act maliciously, they risk losing part or all of their stake.
3. Block Validation
Once selected, a validator proposes a new block. Other validators confirm it. If consensus is reached, the block is added to the chain.
This process keeps the blockchain secure without consuming unnecessary energy.
Key Advantages of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain
Eco-Friendly Architecture
PoS is far more sustainable than PoW. For example, Ethereum’s transition to PoS (Ethereum 2.0) reduced its energy consumption by over 99%.
Decentralized Participation
By removing the hardware barrier, more users can become validators or delegate their tokens to a validator, improving decentralization.
Increased Scalability
PoS networks typically support more transactions per second and enable advanced features like sharding and Layer-2 integrations.
Economic Security
Because validators risk their own capital, they are less likely to act dishonestly, thus aligning network security with economic incentives.
Proof Of Stake vs Proof Of Work
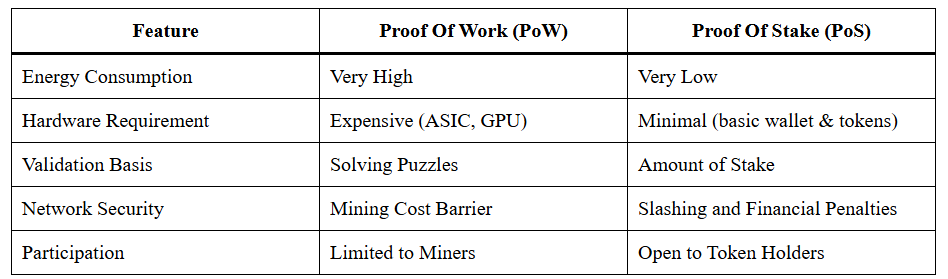
The environmental, economic, and accessibility advantages make Proof Of Stake In Blockchain the preferred consensus model for the future.
Real-World Use Cases of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain
The impact of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain goes beyond theory. Here are some practical applications:

1. Staking-as-a-Service Platforms
Platforms like Lido and Rocket Pool allow users to stake without running a full node. This expands access and supports decentralization.
2. Sustainable NFT Projects
Many NFT platforms are shifting to PoS networks like Tezos and Polygon to support eco-conscious artists and collectors.
3. Cross-Chain Solutions
PoS is powering interoperability-focused chains like Polkadot and Cosmos, enabling seamless communication between blockchains.
These use cases show how Proof Of Stake In Blockchain is already transforming the crypto space.
How to Participate in a PoS Network
Getting involved in Proof Of Stake In Blockchain is simple and rewarding:
- Select a PoS Network: Examples include Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana.
- Get a Compatible Wallet: Wallets like MetaMask, Daedalus, or Phantom support staking.
- Stake Your Crypto: Lock up your tokens either directly or through delegation.
- Earn Rewards: Earn yields in the form of native tokens for supporting network security.
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, PoS offers multiple paths to participation.
Challenges of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain
Despite its advantages, PoS also has some drawbacks:
- Wealth Centralization: Those with more tokens have greater influence.
- Slashing Risks: Validators can lose part of their stake for errors or malicious actions.
- Technical Complexity: Running your own validator node requires technical knowledge.
Still, these challenges are being addressed through innovation and improved network designs.
Regulatory Landscape and Proof Of Stake
As global regulators scrutinize crypto networks, Proof Of Stake In Blockchain may align more favorably with environmental and governance standards. Countries like Germany and Switzerland support PoS models due to their lower energy demands and regulatory transparency.
PoS may soon be the preferred mechanism for networks aiming to comply with ESG standards and governmental guidelines.
Future of Proof Of Stake In Blockchain
Looking ahead, Proof Of Stake In Blockchain is poised to dominate the future of decentralized systems. Here’s what we can expect:
- Mass Adoption: More networks transitioning from PoW to PoS.
- Financial Innovations: Integration into DeFi, DAOs, and Web3 infrastructure.
- Sustainable Development: Stronger support from policymakers and institutions.
The growing ecosystem signals a long-term shift toward more sustainable blockchain models centered on PoS.
Conclusion
Proof Of Stake In Blockchain is not just a technical improvement, it’s a paradigm shift that combines efficiency, inclusivity, and sustainability. It addresses the major limitations of older consensus models and opens up new opportunities for individuals and institutions alike.
As more users and developers embrace this model, the blockchain industry will continue to evolve toward cleaner, faster, and more secure systems, powered by economic incentives rather than brute computational force.
What is Proof Of Stake in Blockchain and how does it work?
Proof Of Stake in Blockchain is a consensus mechanism where validators are selected to confirm transactions and add new blocks based on the number of tokens they stake. Instead of using energy-intensive mining like Proof of Work, PoS relies on participants locking up their tokens as collateral. The more tokens staked, the higher the chance of being chosen to validate, ensuring security through financial incentive.
Is Proof Of Stake more secure than Proof Of Work?
Yes, Proof Of Stake in Blockchain can offer greater economic security. Validators have their own funds at risk, discouraging malicious activity. If a validator behaves dishonestly, they may lose part or all of their staked tokens—a penalty known as “slashing.” This makes attacks on the network economically irrational.
What are the benefits of using Proof Of Stake in Blockchain?
Key benefits include drastically reduced energy consumption, lower hardware requirements, increased transaction scalability, and wider accessibility. Proof Of Stake in Blockchain allows more people to participate in securing the network, which supports decentralization and long-term sustainability.
Can anyone participate in a Proof Of Stake blockchain?
Yes, most PoS networks allow anyone with a minimum stake of the native cryptocurrency to participate. Users can either run a validator node themselves or delegate their tokens to existing validators to earn staking rewards. This makes Proof Of Stake in Blockchain more inclusive than mining-based systems.

I work as a content writer in the blockchain and cryptocurrency domain. I have a keen interest in exploring the world of digital assets, Web3, and emerging crypto technologies. My goal is to provide readers with easy-to-understand, engaging, and trustworthy insights, helping them stay informed and confident in the rapidly evolving world of crypto and blockchain.










